Power and Efficiency
Power
Power is the rate at which work is performed.
P = dU/dt
Pave = ΔU/Δt
Power can also be calculated as F⋅v.
U =∫F⋅r
dr = vdt
P = dU/dt = d( ∫F⋅r)/dt = d( ∫F⋅vdt)/dt = F⋅v
What are the units of power?
Machines are design to perform work at a specified speed or over a range of speeds. The figure below shows a power curve for a typical gasoline engine.
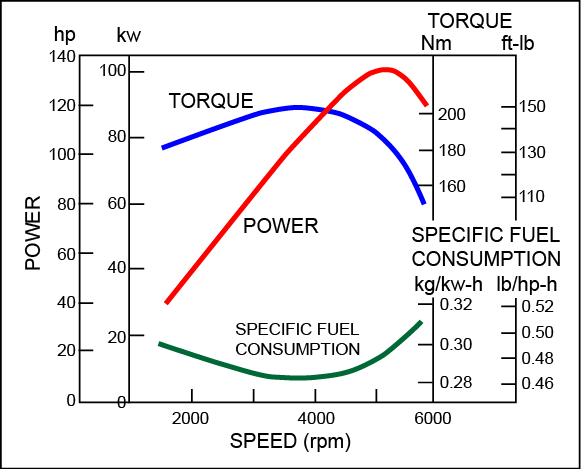
Efficiency
Every machine has losses. For example,
- Friction
- Material deformation
- Wear
- Heat losses
- Incomplete chemical conversion
- Magnetic losses
- Electrical losses
Efficiency is the ratio of the power you get out of a machine divided by the power you put in.
ε = Pout /Pin
Since no machine is perfect, ε < 1.
