General Planar Motion
Under the influence of an unbalanced force and moment, an unconstrained rigid body will translate and rotate. So far, we have considered Euler's second law (the moment equation) for the following cases.
- Pure translation
- Pure rotation
- General planar motion with a center of mass reference
∑MG = 0
∑MP = rG/P x ma
∑MO = IOα
∑MG = IGα
Sometimes it is advantageous to choose an arbitrary reference point (P) that is not the center of mass (G). For example, consider a ladder that slides down a wall as shown in the figure. It may be advantageous to choose point P as a reference to eliminate the normal forces from the moment equation.
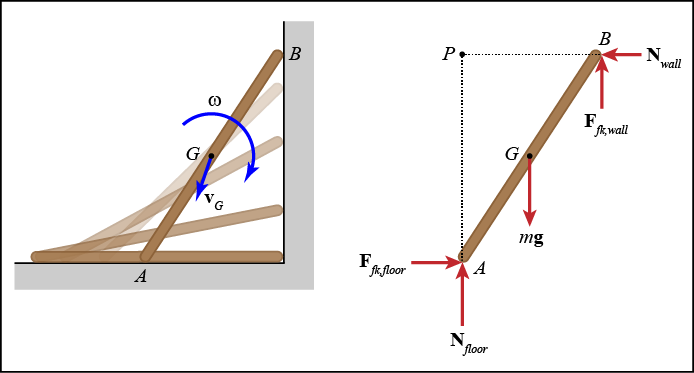
Newton's second law for general planar motion
∑F = maG
Euler's second law for general planar motion
∑MP = IPα + rG/P x maP
or
∑MP = IGα + rG/P x maG
