Rigid-Body Work and Energy - Example Problem 8.5-3
The drum shown has two blocks attached to it with inextensible rope, one to its inner hub and one to its outer hub. Block A has a mass of 50 kg and block B has a mass of 25 kg. The drum has a mass of 10 kg and a radius of gyration about the pin O of kO = 0.30 m. Block A is initially 1.5 m above the floor and is moving downward at 3 m/s. To slow the decent of block A, a force of F = 80 N is applied to the brake arm in the location shown. Determine the speed at which block A hits the floor. The coefficient of kinetic friction at the brake pad is μk = 0.5. (L = 2 m, l1 = 1.7 m, l2 = 0.2 m, ro = 0.3 m, ri = 0.2 m)
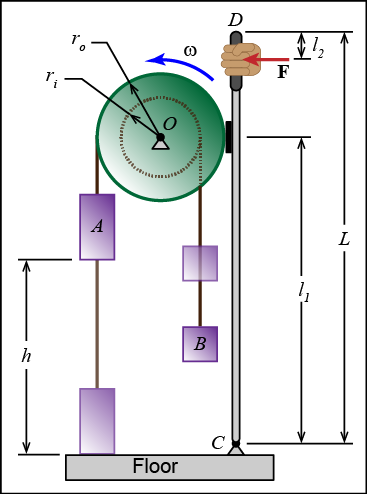
Given:
- mA = 50 kg
- mB = 25 kg
- mD = 10 kg
- kO = 0.3 m
- hA = 1.5 m
- vA,1 = 3 m/s
- F = 80 N
- μk = 0.5
- L = 2 m
- l1 = 1.7 m
- l2 = 0.2 m
- ro = 0.3 m
- ri = 0.2 m
- state 1 = when vA = 3 m/s
- state 2 = after block A has dropped 1.5 m
Find:
- vA,2
Video solution:
The following video walks you through the solution to this problem. It is suggested that you try solving the problem first and then, if you have difficulties with the solution, watch the video for help.
Interactive solution:
