Work-Kinetic Energy Balance - Example Problem 7.3-3
A 40-lb box has a velocity of 10 ft/s when it is at the top of the inclined surface shown, where θ = 40o. The box is acted on by a constant force P = 5 lb that acts at the angle φ = 10o with respect to the inclined surface. Determine the speed of the box after it slides d = 10 ft down the inclined surface. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the plane is μk = 0.4.
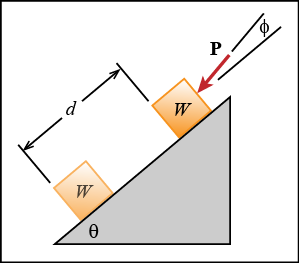
Given:
- W = 40 lb
- v1 = 10 ft/s
- θ = 40o
- φ = 10o
- P = 5 lb
- d = 10 ft
- μk = 0.4
Find: v2
Video solution:
The following video walks you through the solution to this problem. It is suggested that you try solving the problem first and then, if you have difficulties with the solution, watch the video for help.
Interactive solution:
